Generative AI has changed how people discover products and make decisions. Instead of scanning lists of links, users ask ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini or Google’s AI‑assisted search engines for advice and recommendations. These systems synthesize information and often answer questions directly, which means fewer clicks and less visibility in traditional analytics.
Brands that want to stay competitive need to understand how often they are mentioned, trusted and recommended inside these AI‑generated answers and how users reach their sites via AI platforms. The following sections break down the key metrics that matter for AI search and show how to measure them.
AI search key metric comparison table
| Metric | What it measures | Why it matters in AI search |
| AI Visibility | Frequency of your brand’s appearance in AI‑generated answers | Indicates brand recall and presence across AI channels |
| Citation Rate | Percentage of answers linking to your domain among answers that include sources | Signals AI trust and authoritative content |
| Sentiment | Tone of AI descriptions (positive, neutral or negative) | Reveals brand reputation and potential risks |
| Share of Voice | Your share of mentions compared with competitors | Highlights competitive positioning and market momentum |
| AI Search Traffic | Visits referred to your site from AI platforms | Connects AI visibility to user engagement and conversions |
| Bot Activity | Volume and behavior of AI crawlers on your site | Shows content interest, uncovers gaps and informs technical fixes |
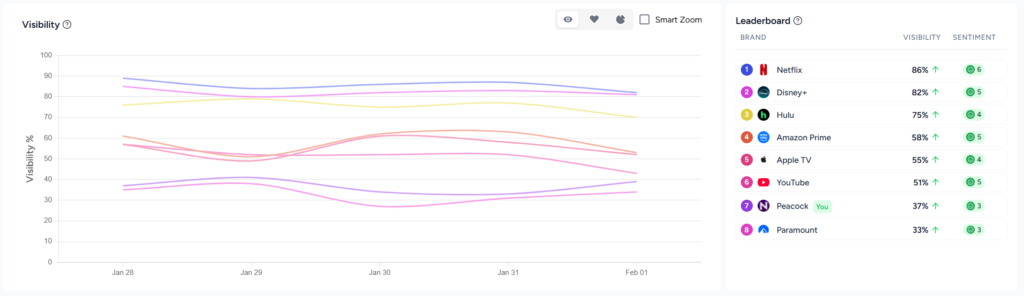
AI Visibility
AI visibility measures how often a brand appears in AI‑generated answers for tracked prompts. High AI visibility indicates strong brand recall by language models even when users never click through to a website.
Definition AI visibility
AI visibility measures how often your brand appears in AI‑generated responses across the prompts and platforms you track.
- Visibility score formula: (Number of responses mentioning your brand ÷ Total responses) × 100.
This calculation provides a baseline for how consistently AI models recall and mention your brand when answering relevant queries. Visibility reflects the distribution of your mentions across different prompts and that consistency over time matters more than sporadic spikes.
Why is AI visibility important?
Visibility is a proxy for brand recognition in the answer era. Higher scores mean AI models frequently recall your brand when discussing your category. Persistent visibility across many prompts indicates stronger authority and improves the likelihood that users will encounter your brand even when they never click a link.
How to track AI visibility
- Define core prompts. Identify 20–30 representative queries for your category and, with a tool like Rankshift, track how often your brand is mentioned in the answers.
- Monitor across platforms. Measure visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini and Google AI Mode—different models draw on different data sets and may rank brands differently.
- Segment by topic and language. Group prompts by intent (educational, comparison, purchase) and by market or language to pinpoint strengths and gaps in your presence.
- Track changes over time. Visibility gains are gradual. Monitor trends weekly or monthly to see whether content updates or outreach efforts improve your presence.
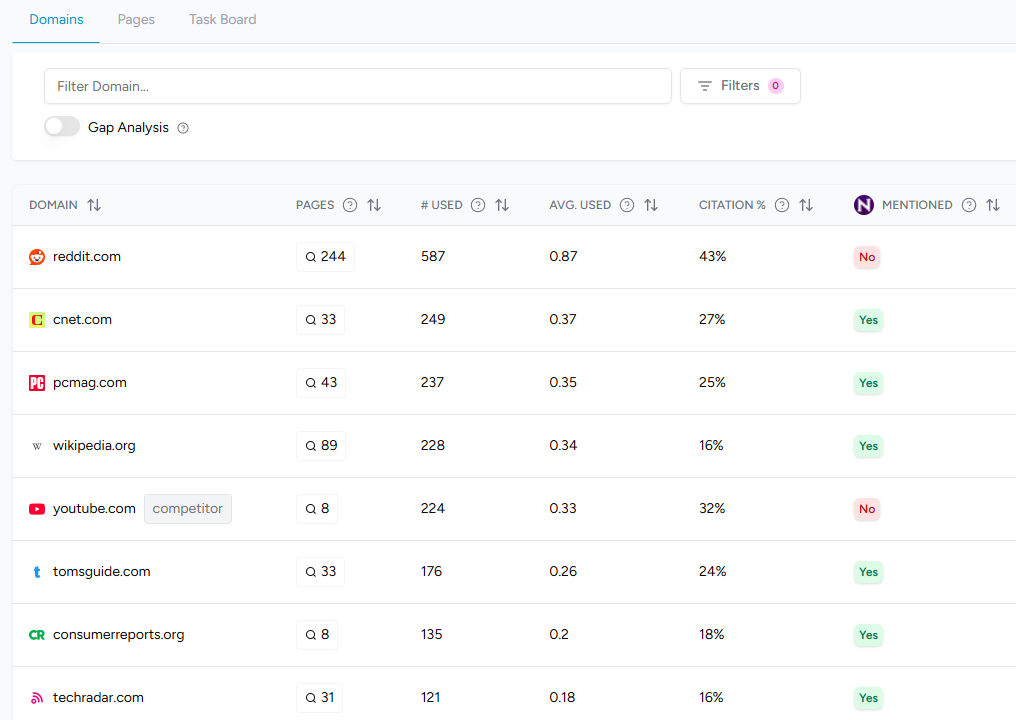
Citation Rate
Citation rate measures the percentage of AI answers that cite a specific URL or domain among answers that include sources. A high citation rate means AI systems trust your content as evidence, giving your brand authority in generative search.
Definition Citation Rate
A citation occurs when an AI response includes a clickable link to the source it used. Citation metrics go beyond mentions; they show which domains AI models trust to support their answers. Rankshift defines citation rate for a given URL as the percentage of answers that cite that URL out of all answers containing at least one citation.
- Citation rate formula: (Answers citing the URL ÷ Total answers with at least one citation) × 100.
At the domain level, multiple page citations are deduplicated. Citation share measures what portion of all citations go to a specific URL, and citation count is the raw number of times the URL appears as a citation.
Why is citation rate important?
Citations signal authority and trust. LLM Pulse explains that AI models choose citations to justify claims, so links in an answer show which sources they rely on. Not every mention leads to a citation; consistent citation across prompts indicates your content is being used to ground AI answers. Tracking citation rate alongside total citation count helps you distinguish between pages that are occasionally linked and those that frequently anchor responses.
How to track it.
- Identify prompts that generate citations. AI responses may not always display sources. For engines that cite sources (Perplexity, Gemini and some ChatGPT tools), capture the responses and note which URLs are linked.
- Calculate domain‑level citation rate. Combine all URLs from your domain and compute how often any page from your domain is cited versus total answers with citations.
- Analyze competitor citations. We recommend monitoring which third‑party pages are cited to understand where AI models learn about your category.
- Prioritize high‑authority pages. Sort pages by citation rate to identify which articles carry authority and which topics may need optimization..
Example. If 28 out of 100 AI answers for a set of prompts include at least one link to your domain, your citation rate is 28 %. A higher rate suggests the AI frequently uses your site as evidence, while a low rate indicates missed opportunities for attribution.
Sentiment
Sentiment gauges whether AI responses talk about your brand positively, neutrally or negatively. Positive sentiment signals trust and credibility while negative sentiment warns of reputational risks.
Definition sentiment
Sentiment measures the tone of AI responses when they mention your brand. Peec.ai assigns a score between 0 and 100, with most brands falling between 65 and 85. The score is calculated by analyzing the language used in the AI response:
- Positive indicators: words such as “trusted,” “reliable,” “innovative” or “leading”.
- Neutral indicators: factual descriptions with little emotional tone.
- Negative indicators: critical language or negative associations.
Why is sentiment important?
Sentiment reveals how AI models frame your brand. Positive sentiment builds trust and credibility, while neutral sentiment maintains professional standing and negative sentiment can erode reputation. Monitoring sentiment alongside visibility and citation rate helps you understand not just whether you are present, but how you are described.
How to track sentiment in AI search
- Gather responses with brand mentions. Collect AI responses that mention your brand across different prompts and platforms.
- Use sentiment analysis. Apply natural‑language processing or specialized tools to score each response based on positive, neutral and negative indicators.
- Compare with competitors. Rankshift emphasizes analyzing sentiment in comparative prompts (“best vs worst”) to see how your brand stacks up against rivals.
- Monitor shifts. Sudden sentiment changes often reflect shifts in public perception, media narratives or competitor positioning. Tracking sentiment over time allows you to respond proactively.
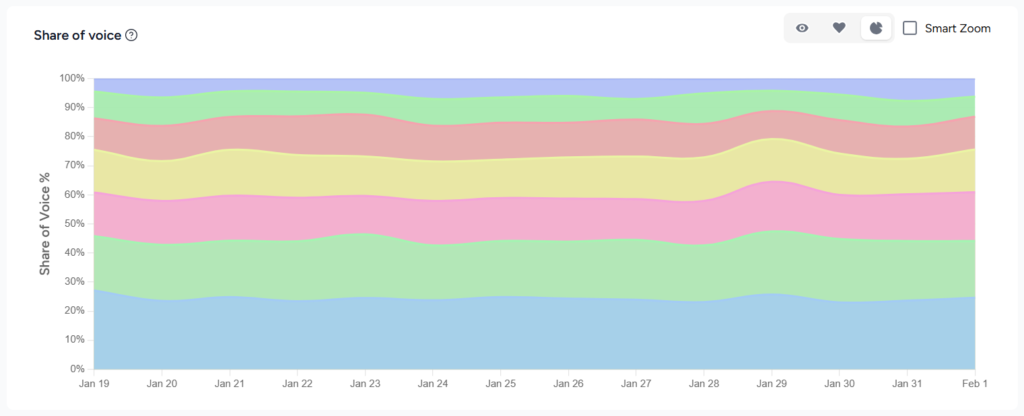
Share of Voice
Share of voice compares how often your brand is mentioned relative to competitors in AI answers. A rising share of voice shows you’re gaining visibility in a crowded field, while a decline signals competitive weakness.
Definition Share of Voice
Share of voice (SoV) measures your brand’s visibility relative to competitors in AI‑generated responses. LLM Pulse defines AI share‑of‑voice as the percentage of brand mentions your company receives compared to all competitors across tracked prompts.
- Share of voice formula: (Your brand mentions ÷ Total brand mentions across all brands) × 100.
Unlike absolute visibility metrics, SoV contextualizes your presence within the competitive landscape. For example, a brand with 100 mentions may have high visibility yet a low share of voice if competitors collectively secure 400 mentions.
Why is share of voice important?
Share of voice is a leading indicator of market perception. Research suggests that brands that dominate conversation eventually dominate market share. A rising SoV means your brand is increasingly favored in AI recommendations, while a low SoV signals vulnerability and risk of being overlooked.
How to track share of voice?
- Define your competitive set. Track direct competitors, category leaders and emerging challengers.
- Segment by prompt category and platform. SoV varies across query types and AI platforms. Analyze educational questions, solution discovery prompts and comparison queries separately to understand where you lead or lag.
- Monitor platform‑specific SoV. Your brand might capture 30 % of mentions in ChatGPT but only 15 % in Perplexity. Use this insight to allocate optimization efforts strategically across platforms.
- Track trends over time. Look for early signals of competitors gaining share, which may foreshadow shifts in market perception.
Traffic from AI Search
AI search traffic measures visits you get from AI‑powered search experiences. Although many users get answers without clicking, tracking traffic from AI platforms links your AI visibility to tangible engagement and conversions.
Definition traffic from AI Search
Traffic from AI search measures visits generated by AI‑powered search experiences to your website. While generative systems often satisfy user intent without clicks, they still send referral traffic when users follow the cited links. We call this AI search engine referral traffic.
Why is AI search engine referral traffic important?
Traffic connects AI visibility to familiar performance metrics such as sessions and conversions. However, a lack of clicks does not imply invisibility; many users get the information they need directly from AI responses. Use traffic as one signal of AI impact, not the sole measure of success.
How to track it.
- Use analytics platforms. Configure Google Analytics 4 or Adobe Analytics to capture referrer data from AI platforms. Tag links in your content with UTM parameters to identify AI sources.
- Monitor by platform and campaign. Segment traffic by AI platform (ChatGPT referrals, Perplexity referrals, Claude referrals) and by campaign or content to see which efforts drive visits.
- Compare with bot impressions. Combined with bot activity (see below), traffic data allows you to estimate click‑through rate (CTR) for AI search: (human clicks ÷ bot hits) × 100.
Bot Activity: Measuring AI Crawlers
Bot activity metrics track how AI crawlers interact with your site, including how often they visit, which pages they fetch and how their behavior changes. Understanding bot activity helps you gauge AI interest in your content, identify gaps and fix technical issues.
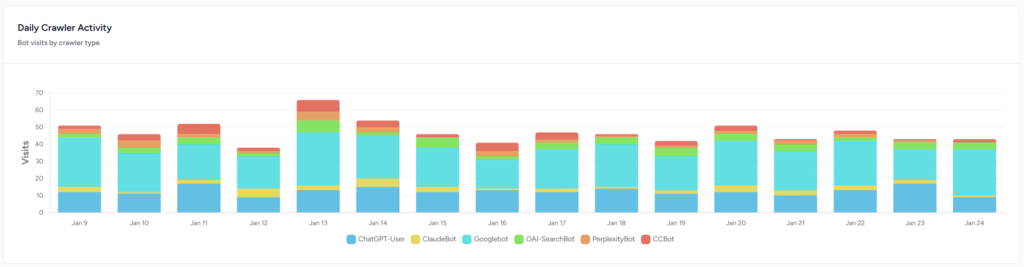
AI bots act as the intermediaries between your content and AI models. Log analysis reveals which AI bots visit your site, what they fetch and how often. We categorize AI bots into three groups: training bots that scrape content for model training, search bots that build indexes, and user bots that fetch pages in real‑time to answer queries. User bots’ visits are a proxy for impressions because each hit represents an attempt to fetch your content for a specific user prompt. Effective bot monitoring involves several metrics:
1. Volume of bot visits and unique pages
- Total requests. Track the total number of requests from AI crawlers. Cloudflare’s AI Crawl Control shows total request volume, volume change and top crawlers by operator. Screaming Frog’s Log File Analyser similarly reports total events and unique URLs crawled.
- Unique pages. Count how many distinct URLs bots hit to gauge how much of your site they explore. We suggest comparing coverage ratios to see which sections receive attention and which remain unexplored.
2. Trends over time
- Time‑series analysis. Cloudflare visualizes successful crawler requests over time, grouped by crawler, category or operator. Monitoring these charts helps you spot spikes after model updates or anomalies in bot behavior.
- Daily/weekly patterns. User bots often follow human usage patterns: they fetch more content on weekdays and during daytime hours. Declining bot activity may signal loss of visibility or technical issues; increasing activity suggests rising interest in your content.
3. Top crawled pages
- Identify high‑demand content. Sort log data by request count to see which pages are most frequently fetched. We discovered that training bots may favor long‑form guides, while citation/user bots target product or commercial pages.
- Align with content strategy. Compare bot‑favored pages with your strategic priorities. If important pages receive little or no bot traffic, improve internal linking or ensure they are not accidentally blocked.
4. Impressions vs. clicks
- Bot hits as impressions. Each visit from an AI user bot represents an impression in a live conversation. Count these hits to estimate how often your content is being considered as a source.
- Estimate click‑through rate (CTR). Divide the number of human clicks (from your analytics) by the number of user‑bot hits to approximate AI search CTR. This provides insight into how often AI‑surfaced recommendations turn into visits.
5. Missed citation opportunities
- Error responses. High numbers of 4xx or 5xx status codes prevent bots from accessing your pages and result in missed citations. Even citation bots, which fetch pages in real‑time to support user answers, will fail to cite your content if they encounter errors.
- Check rendering and accessibility. AI bots often cannot execute client‑side JavaScript, and paywalls or authentication barriers block them entirely. Ensure key pages return a 200 status and render the necessary content server‑side.
6. Gaps in coverage
- Identify uncrawled pages. Compare your site crawl against log files to find pages that rank in Google but never get visited by AI bots. Jérôme Salomon, technical SEO at Oncrawl, emphasizes that differences in crawl behavior between training, search and user bots reveal where AI platforms may be missing your content.
- Prioritize updates. Pages with high SEO visibility but no AI bot visits could benefit from structured data, clearer headlines or translation to the languages that AI models understand.
7. Language and topic segmentation
- Segment by operator and category. Cloudflare’s metrics let you group requests by crawler type, purpose and company. Break down bot traffic by language (if your site serves multiple locales), by article category or page type to see which segments drive AI engagement.
- Tailor content. If user bots fetch mostly English‑language blog posts and ignore product pages in another language, adapt your content or metadata to improve coverage in those segments.
8 – Bot behaviour and updates
- Watch for new user agents. Screaming Frog’s presets list bots like GPTBot (OpenAI training), OAI‑SearchBot (OpenAI indexing), ChatGPT‑User (real‑time response), ClaudeBot (Anthropic), PerplexityBot and others. New bots or updated versions may appear as platforms evolve; tracking them helps you maintain visibility.
- Monitor crawl frequency. AI search bots typically crawl each URL about once per day, while user bots fetch pages on demand. Significant changes in frequency may signal algorithm updates or interest spikes.
- Respect and test robots.txt. Many AI bots follow robots.txt rules, but exceptions exist; some assistants have stopped honoring them entirely. Log analysis will reveal whether bots obey your directives.
- Detect anomalies. Spikes in bot traffic can indicate aggressive crawling or potential abuse. Use response time and IP information to determine whether a particular bot is overloading your server and consider rate limiting or blocking accordingly.
Pulling it Together
No single metric tells the whole story. AI visibility and share of voice show whether you are present in AI answers and how that presence compares to competitors. Citation rate and citation quality reveal whether AI systems trust your content enough to link to it. Sentiment evaluates how your brand is framed when it appears, and traffic connects AI exposure to tangible business outcomes. Bot activity metrics provide the underlying data for impressions and help you diagnose technical or strategic issues.
By tracking these metrics together and segmenting them by platform, topic and time, businesses can understand how generative AI perceives them, where they stand against competitors and what levers to pull to improve their presence. As search shifts toward answers and citations, the brands that thrive will be those who optimize content not just for algorithms, but for the AI models that increasingly mediate how people learn, compare and buy.
Sources
Oncrawl. What log files tell about your visibility in AI search – Jérôme Salomon @ BrightonSEO Autumn 2025. YouTube. January 2026. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=74rcfvhiE5M.
Cates J. AI Search is Changing the Way Marketers Measure Success. Yext. January 2026. https://www.yext.com/blog/2026/01/ai-search-is-changing-the-way-marketers-measure-success.
Salomon J, Salomon J. AI bots explained: What powers platforms like ChatGPT? Oncrawl – Technical SEO Data. https://www.oncrawl.com/ai/ai-bots-explained-what-powers-platforms-chatgpt/. Published January 26, 2026.

