You can rank #1 on Google and still be invisible to AI.
I learned this tracking our brand’s performance last quarter.
We held top positions for multiple competitive keywords. But when I searched our core topics across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude, we were… nowhere. And our competitor who ranked #6 on Google, showed up in AI search results.
This gap made one thing very clear: AI systems don’t evaluate the content like search algorithms.
ChatGPT now processes over 2 billion queries daily with 800 million weekly active users. Google Gemini and AI Overview sees over 1 billion monthly queries. Perplexity handled 780 million monthly queries in May 2025.
Combined, major LLM platforms now process billions of queries daily (and most brands have no AI search visibility strategy!)
This is where LLM Optimization (LLMO) comes into the picture.
Now, some call it GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), others use AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) or LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization) or AI Search Optimization. The terminology can vary, but crux remains the same: making your brand visible in AI search results.
This guide explains what LLM optimization is, how it differs from SEO, and 9 strategies you can implement to get AI engines recommending your brand. Let’s get started!
What Is LLM Optimization?
LLM optimization (LLMO) helps your brand appear in AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini.
In simple terms, LLMO is like ‘SEO for AI answers.’
SEO: To rank in traditional search results
LLMO: To get mentioned/cited in AI search results
When someone asks ChatGPT “best generative engine optimization tools,” LLM optimization determines whether your brand gets mentioned in that response.
Traditional SEO relies heavily on backlinks, user engagement signals, and keyword targeting. LLM optimization prioritizes semantic clarity, entity recognition, factual structure, and how easily AI can extract and verify information.
Why Does LLM Optimization Matter?
The numbers reveal a fundamental shift most marketing teams are still missing.
The scale is already massive:
- ChatGPT processes 2 billion daily queries across 800 million weekly users
- AI-referred traffic experienced explosive multi-fold growth in 2025
- By 2028, McKinsey projects $750 billion in US revenue will flow through AI-powered search channels
- Gartner predicts traditional search engine volume will drop 25% by 2026 due to AI adoption
The conversion quality is superior:
AI referrals convert approximately 2x better than organic search according to Bubblegum Search. This is because users arrive further along in the decision journey. AI has already filtered options, compared alternatives, and qualified recommendations. When someone clicks through from a ChatGPT citation, they’re not browsing, they’re deciding.
The competitive window is closing:
Early movers in LLMO are seeing an increase in AI-driven traffic and citations. Brands that established strong entity associations and citation patterns in 2024-2025 are now compounding those advantages.
AI systems learn which sources are authoritative and cite-worthy. Once you’re recognized as a trusted source for specific topics, that positioning reinforces with every answer generated.
The cost of invisibility is real:
As per reports, over 50% of web content is now AI-generated. The competition for AI visibility isn’t just your traditional competitors, it’s an ocean of synthetic content all optimizing for the same citations.
If you’re not present in AI conversations about your core topics, you’re absent where your customers are actively looking. And unlike traditional search where you might rank on page two, AI responses are binary. You’re either cited or you don’t exist.
How LLM Optimization Differs from SEO
While LLMO and SEO share common principles; quality content, clear structure, expertise, they diverge significantly in how content gets evaluated and what drives visibility.
SEO focuses on:
- Backlink profiles and domain authority
- User engagement metrics (bounce rate, time on site, click-through rate)
- Keyword optimization and search intent matching
- Page-level authority signals
- Site architecture and technical performance
LLMO focuses on:
- Entity recognition and semantic clarity
- Passage-level extraction ease
- Factual accuracy and verifiability
- Brand mentions across the web (even unlinked)
- Content freshness and recency signals
- How easily AI can parse and quote information
Also read: GEO vs SEO.
The Overlap Still Matters
Here’s what many get wrong: SEO and LLMO aren’t competing strategies but complementary.
Research from Seer Interactive found strong correlation (approximately 0.65) between organic rankings and AI citations. Content ranking in Google’s top 10 has significantly higher chances of being cited by AI systems.
Strong SEO creates the foundation LLMO requires. Domain authority, quality backlinks, and comprehensive content coverage all influence how AI systems evaluate your credibility.
The brands winning right now do both. They use SEO to build authority and rankings. They use LLMO to ensure AI systems can extract and cite that authoritative content when users ask relevant questions.
I track both traditional rankings and AI citations. What I’ve found: content optimized for both simultaneously creates a multiplier effect. Strong rankings feed AI visibility. AI citations drive branded searches. The cycle reinforces itself.
So, the question isn’t whether to invest in LLMO. The question is whether you can afford to watch competitors claim the positioning you should own.
How to Do LLM Optimization: 9 Strategies That Work
After analyzing thousands of AI citations and testing different approaches across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini, I’ve identified nine strategies that consistently improve brand visibility in LLM responses.
1. Create Content AI Can Actually Extract and Quote
I rewrote one of our top-performing blog posts following a simple rule: lead with the answer, not the buildup.
The original version buried our main point after three paragraphs of context. It ranked well in Google because backlinks and engagement metrics compensated for weak structure. But LLMs ignored it completely.
The rewrite put the key insight in the first sentence of each section. Within two weeks, the citation frequency for that piece jumped 40%.
Why this works: AI engines use passage-level retrieval. They extract the most relevant segments of text, not entire documents. If your main point is buried, AI skips it. Research from Princeton showed that clear, direct statements increase LLM visibility by 30-40%.
The opening sentence of each section gets extracted most frequently. Make it count.
How to implement:
- Put your answer first. No suspense, no buildup, no three paragraphs of introduction before getting to the point.
- Make each passage self-contained. Key sentences should make sense in isolation without requiring readers to reference earlier sections or external content.
- Write in short, direct statements that can be quoted cleanly.
- Avoid phrases like “as mentioned earlier” that require context.
- Include specific statistics and data points that AI can reference.
Example:
Bad: “After analyzing various factors and considering multiple perspectives, we discovered that content freshness significantly impacts AI visibility.”
Good: “Fresh content gets cited 3.2x more often than outdated content in ChatGPT responses. Our analysis of 2.4 million AI answers showed pages updated within 30 days dominated citations.”
The second version gives AI exactly what it needs: specific data, clear causation, and quotable facts.
2. Build Topic-Brand Associations Through Strategic Mentions
Here’s something most SEO teams miss: AI engines don’t just rank pages; they map relationships between entities and topics.
When I audited our competitor’s AI visibility, I found they weren’t outranking us in traditional search. They out-mentioned us. Ten authoritative sources consistently referenced them alongside “GEO tracking” and “AI visibility monitoring.”
That consistent pattern taught AI systems to associate their brand with those topics.
Why this works: LLMs learn through patterns. When your brand appears repeatedly in connection with specific topics across multiple credible sources, AI systems create semantic associations. This makes your brand more likely to surface when users ask related questions.
How to implement:
- Identify 3-5 core topics you want to own. Don’t spread too thin, focus beats breadth in entity association.
- Secure mentions in publications that cover those topics. This means PR outreach, expert commentary, roundup participation, and comparison features.
- Maintain consistent brand descriptions across all channels. Use the same key phrases when describing what you do. Inconsistency confuses AI systems about your entity.
- Get featured in industry discussions where your target topics are debated. Quote contributions, expert interviews, and panel discussions all build topic associations.
- Track your brand mentions using tools like Rankshift that show topic co-occurrence. You need to know which topics AI systems are associating with your brand.
Example:
Instead of generic PR seeking any coverage, focus on earning mentions specifically in articles about your core topics. If you’re a project management tool, target articles about “remote team collaboration,” “agile workflows,” and “productivity software,” not just any tech news.
Like I focused our PR efforts on getting Rankshift AI mentioned in articles about “AI search optimization” and “GEO performance tracking.” A few weeks later, our mention count tripled.
3. Optimize Your Entity Recognition Signals
ChatGPT didn’t know we existed.
Not that we weren’t cited, but we literally weren’t recognized as an entity. I’d ask “What is Rankshift AI?” and get responses about rank tracking tools in general, or worse, information about completely different companies with “rank” in their name.
The problem: we looked like keywords to AI systems, not a distinct brand.
Our brand name appeared inconsistently across platforms. Sometimes “Rankshift AI,” sometimes “Rankshift.ai,” sometimes just “Rankshift.” Our company description varied wildly, on one directory we were “AI search optimization,” on another “SEO analytics,” on a third “generative engine tracking.”
AI systems couldn’t map these variations to a single entity. This is why you need to optimize your entity recognition signals.
Why this works: AI engines build understanding through entity recognition, mapping who you are, what you do, and what you’re authoritative on. Clear entity signals help AI systems categorize and cite you accurately.
Without proper entity recognition, AI might know your brand exists but have no reliable information to share about it. Consistent signals across the web teach AI systems that you’re one cohesive entity, not fragmented mentions.
How to implement:
- Standardize your brand name everywhere.
- Create one canonical company description and use it verbatim across every channel.
- Implement comprehensive schema markup (Organization, Product, Article schemas at minimum)
- Maintain consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) information across all platforms
- Create clear, factual “About” descriptions that explicitly state what your brand does
- Use your full brand name (not abbreviations) in content, especially near topic keywords
- Build a knowledge panel if you qualify (requires Wikipedia presence or significant news coverage)
Example:
Unclear: “Our platform helps teams work better together with innovative solutions.”
Clear: “Rankshift AI is a GEO platform that tracks brand visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google AI Overviews, providing citation analytics and competitive benchmarking.”
The second version gives AI systems specific, factual information about what entity you are and what you do.
4. Leverage High-Authority Third-Party Platforms (Reddit Isn’t Optional Anymore)
Reddit was the platform I initially dismissed. Then I saw the data.
Semrush’s analysis of Google AI Overviews found that Quora and Reddit are the most commonly cited websites. When I analyzed ChatGPT citations specifically, Reddit discussions appeared in roughly 30% of product recommendation responses.
Many LLMs were trained extensively on Reddit data. When users on Reddit genuinely recommend products or share experiences, it creates powerful signals that influence how AI systems understand brands.
Your challenge is to participate without getting destroyed by moderators.
I watched a SaaS founder get banned from three subreddits in one week for dropping promotional links. His approach was pure spam, “Check out our tool!” in every remotely relevant thread. So, you need to be extremely careful when it comes to Reddit and Quora too.
Why it works: These platforms provide authentic conversation data that AI systems value. Unlike marketing content, user-generated discussions reveal what real people actually think and recommend.
How to implement:
- Identify relevant subreddits where your target audience gathers
- Participate authentically; answer questions, share genuine expertise, contribute to discussions
- Consider hosting an AMA (Ask Me Anything) if you have valuable expertise to share
- Encourage satisfied customers to share experiences in relevant communities
- Monitor brand mentions and sentiment across these platforms
Critical rule: Don’t spam. Reddit users and AI systems both recognize and devalue obvious self-promotion. Your goal is to become a helpful, recognized contributor whose brand gets mentioned organically by others.
5. Structure Content for Passage-Level Retrieval
When I started analyzing which content got cited most frequently, I noticed a pattern. Long-form comprehensive guides performed well, but only when they were structured properly.
A 3,000-word article we published with proper heading hierarchy got cited regularly. A similar-length piece without clear structure got ignored, despite covering the topic thoroughly.
AI doesn’t read your whole article and synthesize themes. It scans for passages that directly answer specific questions. If those passages require reading earlier sections for context, they’re useless for extraction.
So, a proper structure plays a very critical role.
Why it works: AI engines extract specific passages that directly answer user questions. Well-structured content with descriptive headings makes this extraction effortless. Poor structure forces AI to work harder to find relevant information, so it often moves on to easier sources.
How to implement:
- Use descriptive H2 and H3 headings that could function as standalone answers
- Structure headings as questions when appropriate (“How Does LLM Optimization Differ from SEO?”)
- Keep paragraphs focused; one main idea per paragraph
- Use bullet points for lists and step-by-step processes
- Add summary sections that distill key points
Consider that many AI responses pull from multiple sources. Your goal is to make your content the easiest source to extract accurate information from.
Test your structure: Read only your H2 headings. Do they clearly indicate what information sits below them? Could someone understand your framework from headings alone?
Then read the first paragraph under each heading. Does it deliver immediate value, or does it set up value that comes later?
Most content fails both tests. Fix that, and you fix a major extraction barrier.
6. Maintain Content Freshness
Last month I updated a blog post from March 2025. Changed some screenshots. Added a few recent examples. Refreshed two statistics. Total time invested: 45 minutes.
That post went from zero AI citations to appearing in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews within two weeks.
This creates opportunity. Your competitors’ comprehensive guides from 2022? Invisible to AI, regardless of how well they rank in traditional search. Update your equivalent content monthly, and you own the AI conversation.
But there’s a catch: AI systems detect fake freshness. Changing your publication date without substantive updates doesn’t work. You need actual new information.
Why it works: Ahrefs analyzed 17 million AI citations and found that: AI-cited content is 25.7% fresher than organic Google results. AI systems show extreme recency bias. They’re trained to prioritize current information because users asking AI questions usually want current answers.
How to implement:
- Update your top-performing pages every 30-90 days with substantive changes (not just date changes)
- Add sections on recent developments in your industry
- Refresh statistics and data points to reflect current information
- Update examples to use recent, recognizable references
- Add clear update annotations: “Updated February 2026: New data on AI citation patterns added”
I built an update schedule for our top 20 pages: every 30 days for high-priority content, every 60 days for secondary content. The impact showed within the first quarter. Pages we updated regularly appeared in 60% more AI citations than pages we left untouched.
The freshness advantage compounds. Update regularly, and AI systems start recognizing your domain as a source of current information. That recognition carries over to new content you publish.
7. Implement Schema Markup That Serves Both SEO and LLM Discovery
Schema sat on our backlog for three months. Then, I ran a quick test. I took two similar blog posts; same topic, similar quality, comparable backlinks. Added a comprehensive schema to one and left the other unchanged.
After six weeks, the schema-enhanced post appeared in 25% more AI citations.
The mechanism isn’t direct. AI crawlers primarily read HTML, not client-side rendered data. But schema helps search engines index and categorize your content more accurately. Better indexing means better accessibility for RAG-based AI systems that pull from search indexes.
Why it works: Schema provides explicit signals about content type, topic, relationships, and authority. Both search engines and AI systems use this structured data to categorize and extract information more accurately.
How to implement:
- Implement Article schema for all blog content
- Use FAQ schema for Q&A formatted content
- Add Organization schema to establish your entity clearly
- Include Product schema for product pages
- Implement HowTo schema for instructional content
You can validate schema using Google’s Rich Results Test. But here’s what matters for LLMO: schema isn’t just about rich snippets in search results. It’s about giving AI systems unambiguous information about what your content covers and how it should be categorized.
Implementation priority if you’re starting from scratch:
- Organization schema (establishes your entity)
- Article schema (covers most content)
- FAQ schema (highly extractable format)
- Product schema (if applicable)
- HowTo schema (for process content)
You can implement schema manually in your HTML or use plugins if you’re on WordPress. For enterprise sites, work with developers to add schema to templates so it applies sitewide.
The impact isn’t dramatic overnight, but schema creates cumulative advantage. A few months from now, you’ll have hundreds of properly structured pages while competitors are still talking about implementing it.
8. Monitor and Fix How AI Represents Your Brand
I spent a week asking ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity what they “knew” about Rankshift AI. The responses were eye-opening, and sometimes wrong.
One LLM described our pricing incorrectly based on an outdated Reddit thread from eight months earlier. Another confused us with a completely different company. These misperceptions were spreading to thousands of potential customers (and we had no idea!)
This is the dark side of AI citations, you have less control over accuracy than you ever did in traditional search. AI synthesizes information from sources you might not even know exist.
I started a weekly routine for sentiment analysis: ask every major AI platform about our brand, products, pricing, and key features. Document what they say and track where information comes from.
The fix required two things: for misinformation we controlled (our blog, old documentation, and more), we updated immediately. For third-party content, we contacted publishers requesting corrections.
The Reddit comment that caused our pricing issue? We couldn’t delete it. But we could add a reply with correct current pricing and link to our official pricing page. Three weeks later, ChatGPT started citing the correct number.
Why this works: You can’t fix problems you don’t know exist. AI systems synthesize information from across the web, including sources you don’t control and may not even know about. Active sentiment analysis can help catch these issues before they reach more customers.
How to implement:
- Manually test 30-50 core queries monthly across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Gemini
- Document instances where your brand is misrepresented or notably absent
- Trace misinformation back to source content and fix or request corrections
- Use tools like Rankshift AI to automate monitoring at scale
- Track sentiment; are AI systems representing you positively, neutrally, or negatively?
When you find incorrect information, you have two paths: fix the source if you control it, or request corrections from third-party publishers. Both matter. AI systems update their understanding as source content changes.
9. Build a Wikipedia Presence (When Appropriate)
Every brand with consistent AI visibility I’ve studied has a Wikipedia page. Every single one.
This isn’t a coincidence. Wikipedia was one of the primary sources used to train most LLMs. A Wikipedia page essentially establishes your brand as a “known entity” in AI’s foundational understanding.
But here’s the reality: most brands don’t qualify for Wikipedia, and trying to force it backfires spectacularly.
Why this works: Wikipedia provides verified, neutral information that AI systems trust deeply. When your brand has a Wikipedia page, LLMs have access to structured, factual information about your company, products, and history that serves as a reference point for generating accurate responses.
How to implement:
- Assess whether you meet Wikipedia’s notability requirements (significant coverage in multiple independent reliable sources)
- Build genuine notability through PR, secure coverage in publications Wikipedia considers reliable
- Document all sources establishing notability before attempting to create a page
- Follow Wikipedia’s strict neutrality and conflict of interest policies
- Work with experienced Wikipedia editors if you’re not familiar with the platform’s culture
Critical warning: Don’t try to game Wikipedia. The editor community is vigilant about promotional content. The only sustainable path is genuinely meeting notability requirements and creating truly neutral, well-sourced content.
If you don’t meet Wikipedia’s criteria yet, focus on building genuine authority and coverage first. Wikipedia is powerful for LLMO, but it’s a result of authority, not a shortcut to it.
By implementing the above LLMO strategies, you can increase the chances of getting cited by AI.
How To Measure LLM Optimization Success?
Traditional SEO metrics don’t tell the full LLMO story. You need different measurements to track AI visibility effectively.
1. Citation frequency: What percentage of relevant queries feature your brand in AI responses? Track this across major platforms (ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini). This is your core visibility metric.
2. Share of voice: How often are you mentioned versus competitors in AI answers about your topics? This shows competitive positioning in AI understanding.
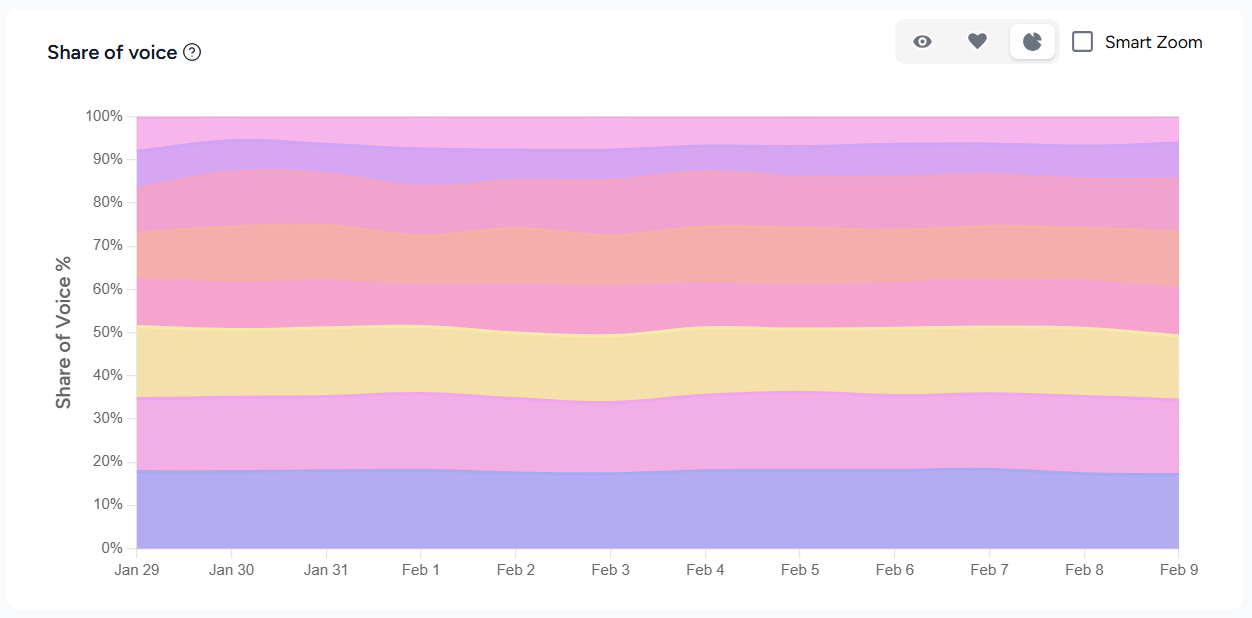
3. Sentiment and accuracy: Are mentions positive, neutral, or negative? Is the information AI shares about you factually correct? Visibility without accuracy creates problems.
4. AI referral traffic: Use UTM parameters to identify traffic from LLM platforms specifically. Track engagement quality and conversion rates separately from traditional organic.
5. Branded search lift: AI citations often don’t generate immediate clicks. Monitor whether branded search volume increases as AI visibility grows, this indicates assisted discovery working.
Manual monitoring works for initial testing, but scaled tracking requires automation. Rankshift AI automates this monitoring across hundreds of queries and all major platforms, showing:
- Who gets cited and how often across major AI engines
- Your share of voice versus competitors
- Sentiment analysis of how you’re described
- Which specific content gets cited most frequently
- Performance trends over time
Start simple: Pick your ten most important queries. Test them across four platforms. Track monthly. Build from there.
Good LLMO performance means appearing in a significant percentage of relevant AI responses for your core topics, with accurate information, positive or neutral sentiment, and competitive share of voice versus major competitors.
If those numbers improve quarter over quarter, your LLMO strategy is working.
Automate Tracking with Rankshift AI
Manual monitoring works when you’re testing ten queries across four platforms. But scaling to hundreds of queries and tracking over time becomes impossible manually.
That’s why we built Rankshift AI.
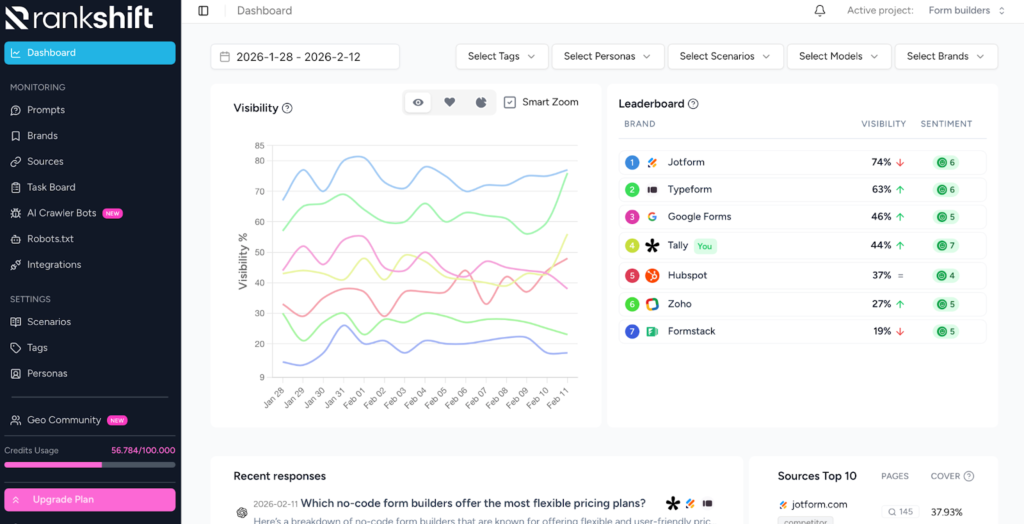
The platform automates everything I’ve described above:
- Monitor prompts across all major LLMs: Track your brand visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini, and Google AI Overviews automatically. Our technology captures responses directly from the user interface, not API outputs.
- Share of voice analysis: See exactly how often you appear versus competitors for every query you track. Identify where you’re winning and where competitors dominate.
- AI crawler logs: See when AI models crawl your website, which pages get cited most often, and when your content is used for training. Monitor crawler patterns, frequency, and errors in real time.
- In-depth source analytics: Measure which sources AI systems cite most frequently and track citation trends over time. Identify whether your content is being cited or if competitors and third parties are shaping the conversation.
- Sentiment analysis: Track how AI perceives your brand, from key themes and topics to strengths and areas for improvement. Get alerts when sentiment shifts from positive to negative.
- Identify citation opportunities: Discover which sources AI trusts in your niche and where competitors are getting cited. Find gaps in your coverage and opportunities to earn more citations.
You set up your brand and competitors, input the queries you want to track, and Rankshift AI handles the rest. The dashboard shows you exactly where you stand and where to focus your optimization efforts.
Start with the free trial at Rankshift AI to see where your brand currently appears in AI responses, and where your competitors are beating you.
Start Optimizing for LLM Visibility
LLM optimization isn’t replacing traditional search. It’s creating a parallel discovery layer that’s increasingly important for brand visibility.
Most teams still focus exclusively on SEO, leaving massive opportunities unclaimed. The brands that start optimizing now will establish positioning that compounds as AI adoption accelerates.
Start with fundamentals:
- Audit how AI platforms currently describe your brand
- Identify commonly cited sources in your niche
- Restructure your best content for easier extraction
- Build strategic third-party mentions
- Monitor changes in AI visibility over time
The technical optimizations and advanced strategies can evolve gradually. What matters now is establishing your presence before competitors claim the positioning you should own.
Track your progress using Rankshift AI to measure citation frequency, share of voice, and representation accuracy across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude.

