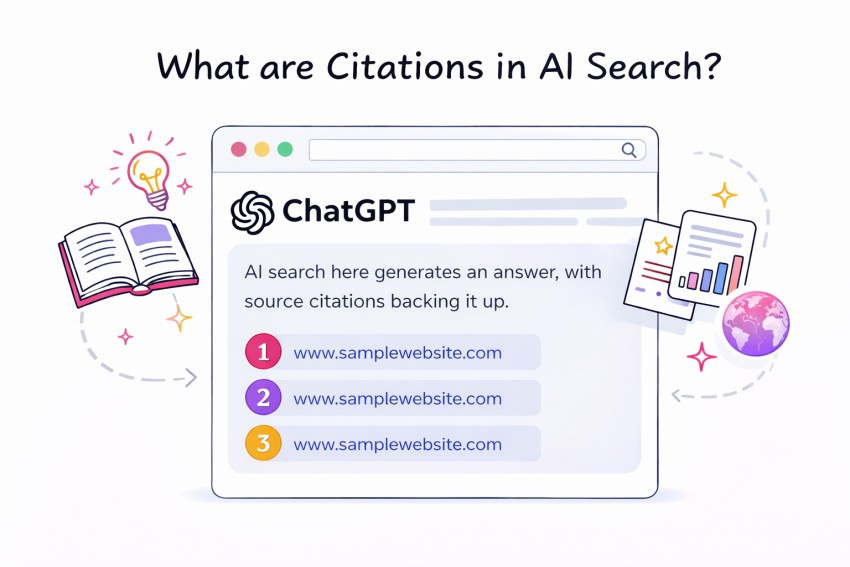
Citations in AI search are the visible sources behind an answer. They show up as cards, links, or footnotes inside the response itself, not buried in a page or hidden behind anchor text.
That shift matters.
In generative search, visibility no longer comes from ranking highest on a results page. It comes from being included in the answer. When an AI cites your content, your site is no longer just a destination, it becomes part of the explanation. Traditional backlinks still signal authority, but citations decide who gets seen when users stop scrolling and start asking.
This is what makes citations the closest thing we have to a new backlink, and why they now sit at the center of AI search visibility.
Generative search and the shift in search behaviour
Generative search tools create answers by synthesising information from multiple sources and citing them directly. They no longer return a simple list of blue links; instead, they deliver summaries with source cards, transforming how people discover information.
Traditional search engines return a ranked list of links. AI search tools such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini and Google’s AI Overviews work differently. They synthesise answers from multiple sources and display references directly in the answer.
This shift is dramatic. An analysis of over 36 million Google AI Overviews and 46 million citations showed that the feature grew from appearing in just 6.49 % of searches in January 2025 to more than half of all queries by October 2025.
Despite that surge, high citation frequency does not necessarily deliver traffic; Wikipedia remained the most‑cited domain with more than 1.1 million mentions but still saw an 8 % decline in page views. The example highlights how generative engines upend the established link‑click model.
Optimising for these AI‑driven experiences requires a new discipline known as generative engine optimisation (GEO). GEO focuses on making content extractable, trustworthy and quotable so that AI systems cite it. Citations replace traditional keyword rankings as the most visible signal of authority. This article explains what AI citations are, why they matter, how to measure them and how to earn them.
What is an AI citation?
An AI citation is a visible reference to a source used by an AI search engine. It shows readers where the answer originated and differs from backlinks by being displayed within the AI summary rather than hidden in web content.
Citations can take several forms:
- Name‑drop mentions: the AI mentions your brand or product in its response.
- Source references: your URL appears in a “works cited” list beneath the answer.
- Quoted passages: the AI includes a verbatim excerpt from your content and credits you.
- Synthesised mentions: your insights influence the narrative without an explicit link.
An AI citation is not a guarantee of traffic, nor is it simply a backlink. It is a visible signal within the answer itself that tells users (and algorithms) where the information came from. Because generative engines synthesise content, they often cite pages that never ranked for the query in classic search.
An Ahrefs study of 15,000 long‑tail queries found that only 12 % of the links cited by ChatGPT, Gemini and Copilot overlapped with Google’s top‑10 results for the same prompts; four out of five citations pointed to pages with no ranking presence. In other words, citation probability does not correlate with traditional SEO rankings.
The importance of AI citations even without clicks
AI citations matter because they determine visibility in zero‑click answers. Being cited exposes your brand to users even when they do not click through and signals that your content is credible.
Generative engines are becoming the first impression for many users. Yoast notes that people often see an AI summary before they see any search results. Being cited means your brand becomes part of that first interaction.
AI citations deliver several benefits:
- Visibility without clicks: prompt‑driven search encourages users to seek direct answers rather than click through to websites. By being cited, your brand appears in front of users even if they never visit your site. This visibility also builds brand recall even when users do not click.
- Credibility and trust: citations signal that AI systems consider your content trustworthy. Being listed as a source or quoted in an answer boosts perceived expertise.
- Authority signals: generative engines factor structured data, domain authority and external trust signals into citation selection. Quality content with strong E‑E‑A‑T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness) attributes is more likely to be cited.
- New form of referral: while backlinks still matter for SEO, AI citations function as a new type of referral. They influence brand perception and can drive assisted conversions even when direct traffic is low.
Importantly, citations are highly volatile. iPullRank’s analysis shows that two identical queries on different days can produce different AI citations. AI retrieval is probabilistic: systems fan out queries into variations, retrieve passages based on semantic embeddings and then choose which passages to cite using statistical weighting.
This variability means inclusion can “flicker on and off with no obvious explanation”, making continuous monitoring essential.
Measuring visibility in AI‑generated answers
Visibility in AI‑generated answers is measured by tracking mentions, citations and share of voice rather than keyword rankings. Because AI results vary by prompt and time, monitoring tools focus on presence and context across multiple platforms.
New AI serach metrics are needed to measure presence across AI platforms. Rankshift, an AI visibility tool, emphasises tracking prompts, citations and competitor benchmarks rather than keyword positions. Key monitoring concepts include:
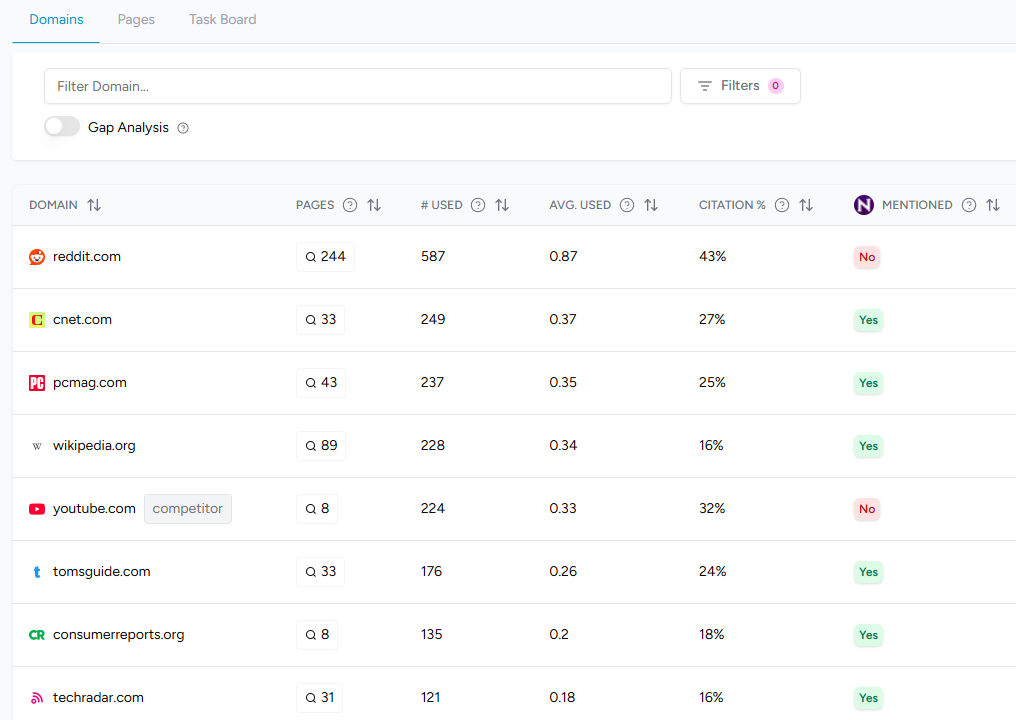
Brand Mentions and Citations
We recommend tracking both mentions (occurrences of your brand name without a link) and citations (linked references to your content) across AI platforms. Mentions indicate awareness and authority; citations validate that the AI trusts your content.
Prompt‑Triggered Visibility and Context
Monitoring which prompts trigger your brand and how you are represented helps tailor content to user intent. The context of the mention, whether your brand is a top recommendation or buried in a list, shapes perception and influences conversions.
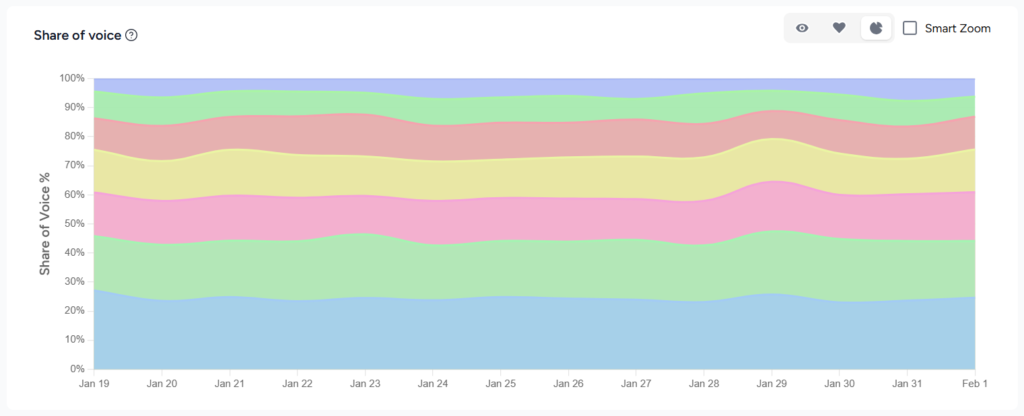
Share of Voice Over Time
Share of voice measures the proportion of AI answers in your niche that include your brand compared with competitors. Tracking citation and mention trends over time reveals whether your optimisation efforts are improving visibility. Visibility trends can also show how algorithm changes affect your presence.
Link Destination and Depth
Analysing which of your pages AI models cite, like home pages, blog posts, product pages, helps prioritise optimisation. Log file analyzers for AI bots and AI visibility tools can reveal how often models access your site and which pages provide training data.
Manual Audits and Brand Monitoring
No universal tool tracks citations across all AI platforms. We recommend combining GA4 segmentation, manual query audits, brand monitoring tools and competitive analysis. Manual audits involve running your core queries across different AI search engines and recording whether your domain appears. Brand‑mention tools (Brand24, Mention, Talkwalker) can alert you when your brand is referenced in published content that AI may later cite.
Citation rate and key metrics
Citation rate is the share of AI answers that reference your domain. You calculate it by dividing the number of cited answers by the total answers in your sample window, and you complement it with related metrics to gauge overall visibility.
Citation rate formula = (number of AI answers that cite your domain ÷ total number of monitored AI answers) × 100
To measure performance in AI search engines, marketers use a set of key AI search metrics tailored to citation visibility. These metrics go beyond page rankings to assess how often and how well AI engines surface your brand. The table below summarises key metrics, what they measure and why they matter.
| Metric | What it measures | Why it matters |
| AI citation rate | Percentage of AI answers that reference your domain (citations ÷ answers). | Indicates how often you are referenced; key indicator for AI visibility. |
| Response inclusion rate | Fraction of prompts that include your brand (included prompts ÷ total prompts). | Shows how widely your brand appears across queries. |
| Entity‑recognition accuracy | Ratio of correctly recognised entities to all recognised entities. | Measures whether AI systems interpret your structured data correctly, which improves citation precision. |
| Visibility score | Combined metric from tools like Rankshift capturing your presence across AI platforms. | Helps benchmark your share of voice relative to competitors. |
Generative engine optimization, the discipline of designing content for AI citation, encourages tracking these metrics over time to identify improvements and spot declines.
Earning citations in generative search
To get cited as a source in AI search, you need to produce content that is extractable, authoritative and recognisable by AI. Generative engine optimisation (GEO) emphasises clear structure, expert signals and active monitoring.
Optimising for citations involves making your content easy for AI models to extract, understand and trust. Recommendations drawn from Yoast, Rankshift and iPullRank include:
- Create deep, original and useful content: publish unique research, case studies and interviews. AI models favour fresh problem‑solving content.
- Write for real questions, not just keywords: structure content around the questions your audience actually asks. Conversational, direct answers make your content more likely to be selected by AI.
- Leverage structured data and schema markup: include FAQ, HowTo, Article or Product schema to help AI and search engines interpret your content. Strapi notes that monitoring schema validation pass rates helps catch technical issues that affect citations.
- Build relationships and authoritative mentions: earn backlinks and inclusion in authoritative lists, review sites and directories. Authority signals from trusted publications increase your chances of being cited.
- Use clear, quotable statements: craft short, memorable definitions, statistics and explanations that models can lift verbatim. Structured layouts with subheadings and bullet points improve extractability.
- Keep content fresh and aligned with E‑E‑A‑T principles: update articles regularly, show expertise through author bios and case studies, and provide transparent references.
- Monitor and adapt: track citation and visibility metrics, identify prompts where competitors are cited and refine your content accordingly. Strapi recommends integrating GEO monitoring into your CI/CD pipeline so that failing schema tests or citation rate drops automatically trigger reviews.
Strategic implications of generative search
Marketers love a clean metric. For years, that metric was rankings. Position one meant visibility, authority, traffic. Simple.
AI search breaks that simplicity.
Scroll LinkedIn and you’ll see the same pattern repeating itself: people arguing about tools, frameworks, and acronyms. GEO versus SEO. Citations versus backlinks. As if one replaces the other.
That framing misses the point.
SEO is still the foundation. Always has been. The things that help a page rank, authority, clarity, structure, relevance, still matter in generative search. Weak SEO almost never earns strong AI citations. You cannot shortcut trust.
But strong SEO alone is no longer enough.
We are already seeing brands with excellent rankings, clean link profiles, and textbook optimization get ignored by ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI Overviews. At the same time, less visible competitors dominate citations simply because their content is easier to extract, easier to quote, and easier to trust in an answer-first environment.
The difference is the outcome you optimize for.
SEO optimizes for clicks from a list of links. Citations optimize for inclusion inside the answer itself.
That shift changes what visibility means. It changes how authority is expressed. And it changes how success should be measured.
This is not about replacing SEO. It is about understanding that generative search rewards a different kind of clarity. If rankings were about being the best result, citations are about being the best source.
And that distinction is now impossible to ignore.
Sources
Kuryatnik V. Most cited domains in Google AI Overviews: 2025 Traffic Impact analysis. Digital Marketing Agency for Predictable Growth. https://thedigitalbloom.com/learn/google-ai-overviews-top-cited-domains-2025/. Published December 19, 2025.
Qureshi A. Everything you need to know about AI citations vs backlinks. Yoast. https://yoast.com/ai-citations-vs-backlinks/. Published October 1, 2025.
Iwuozor J. Probability in AI Search: How Generative Engine Optimization reshapes SEO. iPullRank. https://ipullrank.com/probability-ai-search. Published October 10, 2025.